How to Start Investing in the Indian Stock Market: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction
The Indian stock market has grown into one of the world’s most dynamic financial ecosystems, offering lucrative opportunities for investors of all levels. With two primary exchanges—the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE)—India’s stock market is home to thousands of companies across various sectors. From multinational giants to emerging startups, the market offers diverse investment avenues to help individuals build wealth over time.

Alt txt: A high-quality digital illustration of a young professional investor exploring the Indian stock market. The investor, dressed in business casual attire, looks confident while analyzing investment options.
Why Invest in the Indian Stock Market?
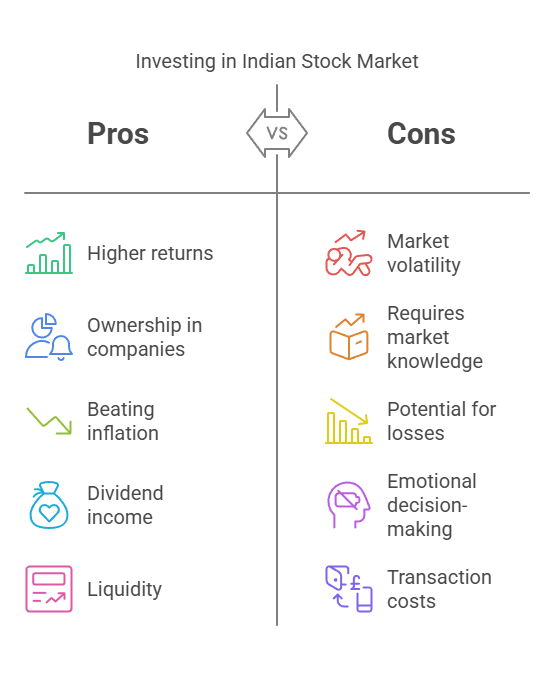
Investing in the Indian stock market allows individuals to grow their wealth beyond traditional savings accounts or fixed deposits. Some key benefits include :
- Higher Returns Compared to Traditional Investments – Over the long term, equities have outperformed fixed-income instruments like bank deposits.
- Ownership in Companies – Stock investments give you a stake in some of the most successful businesses.
- Beating Inflation – Stocks have historically provided better returns than inflation, preserving purchasing power.
- Dividend Income – Some stocks offer regular payouts, adding passive income to your portfolio.
- Liquidity – Unlike real estate or other investments, stocks can be easily bought or sold on exchanges.
Also if you want to know more What is the Indian Stock Market, and How Does It Work? click here
Common Misconceptions About Stock Market Investing
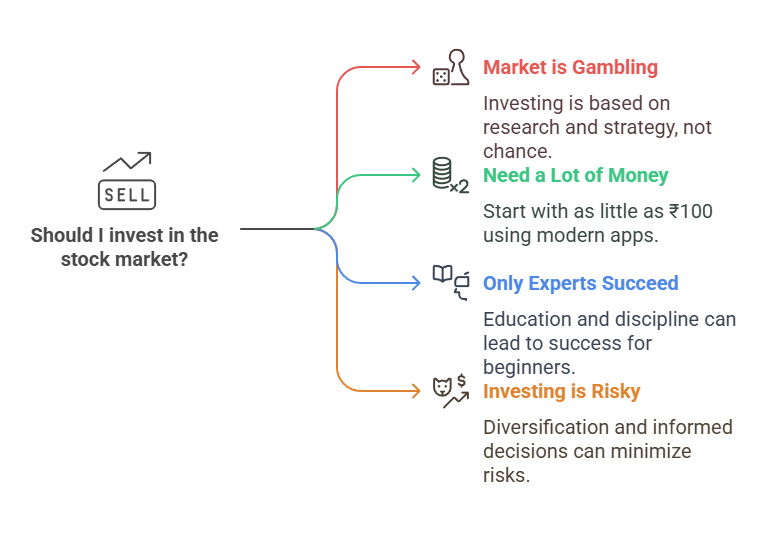
Many beginners hesitate to invest due to myths surrounding the market. Here are some misconceptions debunked:
- “Stock Market is Just Gambling” – Unlike gambling, investing is based on research, strategy, and company performance.
- “You Need a Lot of Money to Start” – With modern trading apps and fractional investing, you can start with as little as ₹100.
- “Only Experts Can Make Money” – With proper education, research, and discipline, even beginners can succeed.
- “Investing is Risky” – While all investments carry risk, diversification and informed decision-making help minimize losses.
With the right approach, knowledge, and risk management, anyone can start investing in the Indian stock market. This guide will walk you through the entire process—step by step—to ensure a smooth and informed entry into the world of investing.
Step 1: Choose a Reputable Broker
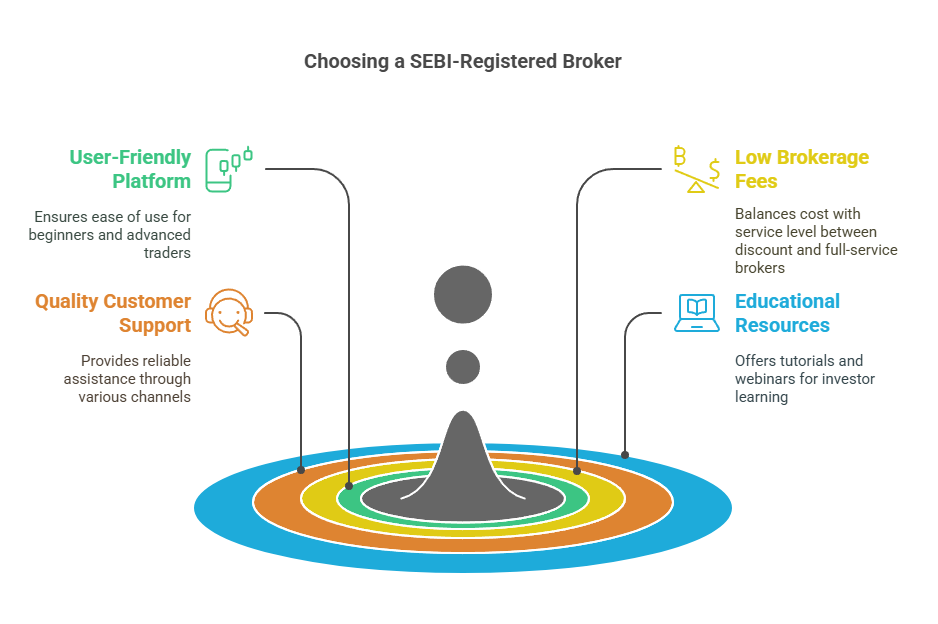
Selecting a SEBI-registered broker is the first step to investing in the Indian stock market. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates brokers to ensure fair trading practices, making it essential to choose a registered and reliable platform.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Broker
- User-Friendly Trading Platform
- Look for an intuitive interface, especially if you are a beginner.
- Ensure the broker offers a well-designed mobile app for trading on the go.
- Advanced traders may prefer platforms with technical charting and analysis tools.
- Low Brokerage Fees
- Discount Brokers (e.g., Zerodha, Upstox, Groww) offer lower fees but provide only basic trading services.
- Full-Service Brokers (e.g., ICICI Direct, HDFC Securities, Kotak Securities) provide research reports, investment advice, and additional support but charge higher fees.
- Compare brokerage charges for different types of trades, including delivery, intraday, and derivatives.
- Quality of Customer Support
- Ensure the broker provides prompt and reliable customer service via multiple channels (chat, phone, email).
- Check online reviews and customer feedback before making a decision.
- Availability of Educational Resources
- Some brokers offer investment tutorials, webinars, and market analysis to help new investors learn.
- If you are a beginner, choosing a broker with strong learning support can be beneficial.
Comparison of Popular Brokers in India
| Broker | Type | Brokerage Fees | Platform & Features | Best For |
| Zerodha | Discount | Low | Easy-to-use, Kite app | All investors |
| Upstox | Discount | Low | Fast execution, mobile-friendly | Beginners |
| Groww | Discount | Zero brokerage on equity delivery | Simple UI, great for beginners | New investors |
| ICICI Direct | Full-Service | Higher fees | Research-backed, strong support | Serious investors |
| HDFC Securities | Full-Service | Higher fees | Banking integration, research tools | HDFC account holders |
Step 2: Open a Demat and Trading Account
To trade in the Indian stock market, you need two accounts:
- Demat Account – Holds your shares in electronic form, similar to a digital locker.
- Trading Account – Enables buying and selling of stocks on stock exchanges like NSE and BSE.
Most brokers provide both accounts as part of their services.
Documents Required for KYC Verification
To comply with SEBI regulations, brokers require investors to complete the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. The necessary documents include:
- PAN Card – Mandatory for stock trading in India.
- Aadhaar Card – Used as proof of identity and address.
- Bank Account Details – A cancelled cheque or recent bank statement for linking your trading account.
- Photograph and Signature – Needed for verification purposes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your Account
- Choose a Broker – Select a SEBI-registered broker based on your needs.
- Visit the Broker’s Website or App – Most brokers provide an online account opening process.
- Fill Out the Application Form – Enter your personal details, PAN, Aadhaar, and bank information.
- Upload KYC Documents – Submit scanned copies of PAN, Aadhaar, and other required documents.
- Complete e-KYC Verification – Some brokers allow Aadhaar-based OTP verification for a quicker process.
- Sign the Agreement Digitally – Review and accept the broker’s terms and conditions.
- Wait for Approval – The broker verifies your details, which usually takes 24–48 hours.
- Start Trading – Once approved, you can log in to your account, deposit funds, and begin investing.
By completing these steps, you will have a fully functional Demat and trading account, enabling you to invest in the Indian stock market with confidence.

Step 4: Research and Select Stocks
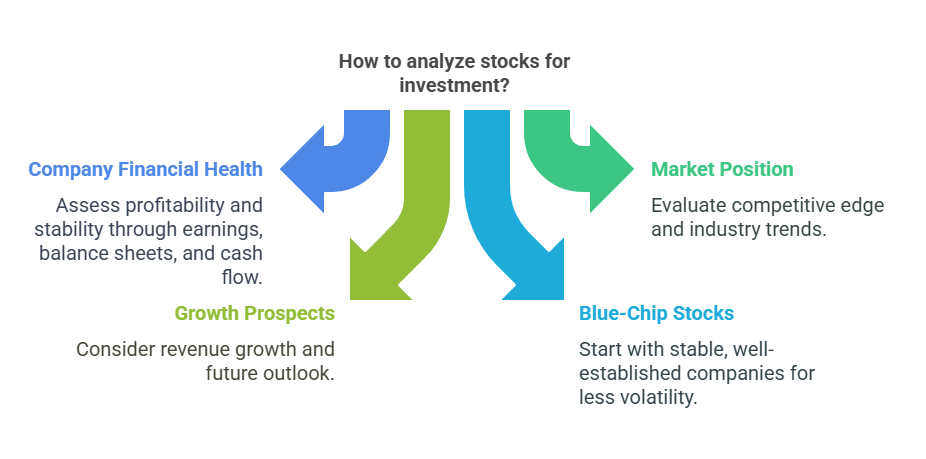
investing in the Indian stock market requires careful research to identify strong companies with growth potential. Before buying any stock, analyze the following key factors:
1. Company Financial Health
- Earnings Reports – Review quarterly and annual earnings to assess profitability.
- Balance Sheets – Check assets, liabilities, and debt levels to evaluate financial stability.
- Cash Flow Statements – Ensure the company generates consistent cash flow for operations.
2. Market Position
- Competitive Edge – Look for companies with strong brand recognition, innovation, or unique products.
- Industry Trends – Understand the sector’s overall performance and future potential.
- Economic Conditions – Consider how inflation, interest rates, or government policies affect the company.
3. Growth Prospects
- Revenue Growth – Companies with increasing revenues over time signal long-term potential.
- Sector Performance – Fast-growing industries, like technology and renewable energy, may offer better opportunities.
- Future Outlook – Read analyst reports and company guidance for insights into expected growth.
4. Importance of Blue-Chip Stocks
For beginners, it is advisable to start with blue-chip stocks—large, well-established companies with a history of stable returns (e.g., Reliance Industries, TCS, HDFC Bank). These stocks tend to be less volatile and provide steady growth.
5. Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis – Focuses on evaluating a company’s financial statements, management, and market conditions.
- Technical Analysis – Uses stock price charts, trends, and trading patterns to predict future movements.
- Which One to Use? – Long-term investors prefer fundamental analysis, while short-term traders use technical indicators.
Step 5: Decide Your Investment Amount
Determining how much to invest is just as important as selecting the right stocks. A well-planned investment strategy helps manage risks and maximize returns.
1. Setting Realistic Financial Goals
- Define your investment horizon (short-term or long-term).
- Decide whether you are investing for wealth creation, retirement, or short-term gains.
- Avoid investing money you may need in the near future.
2. Diversification Strategy to Minimize Risks
- Spread investments across different sectors (e.g., IT, banking, healthcare).
- Avoid putting all your money into a single stock, as this increases risk.
- Consider investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds for automatic diversification.
3. Risk Assessment and Portfolio Allocation for Beginners
- Conservative Investors – Focus on blue-chip stocks and dividend-paying companies.
- Moderate Investors – A mix of stable stocks and some high-growth stocks.
- Aggressive Investors – Higher allocation to small-cap and growth stocks, with higher risk exposure.
A well-balanced portfolio ensures that you are not overly dependent on a single stock or sector, reducing the impact of market volatility on your investments.
Step 6: Place Your First Trade
Once you’ve selected a stock and decided how much to invest, it’s time to place your first trade. This process happens through your broker’s online trading platform, which allows you to execute buy and sell orders efficiently.
How to Place an Order
- Log in to your trading account – Access your broker’s platform via a desktop or mobile app.
- Search for the stock – Use the stock’s ticker symbol to find it in the trading interface.
- Choose the order type – Select from different types of trade orders (explained below).
- Enter the quantity – Decide how many shares you want to buy or sell.
- Review and confirm – Double-check your order details before executing the trade.
Types of Orders
- Market Order – Buys or sells the stock immediately at the current market price. This ensures execution but may lead to price fluctuations.
- Limit Order – Sets a fixed price at which you want to buy or sell. The order executes only if the stock reaches that price, helping you control your entry and exit points.
- Stop-Loss Order – A risk-management tool that automatically sells your stock if the price drops to a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
Step 7: Monitor and Manage Your Investments
Investing doesn’t end with buying stocks; active monitoring and management are essential for long-term success.
Tracking Stock Performance
- Regularly check stock prices and market trends using your broker’s app.
- Follow financial news, earnings reports, and economic updates that impact stock prices.
- Use technical indicators like moving averages and RSI (Relative Strength Index) to assess stock momentum.
Using Broker Tools and Market Resources
Most brokers offer features such as portfolio tracking, stock screeners, and analytical charts. Additionally, resources like financial news websites, expert analysis, and investment forums can provide valuable insights.
Adjusting Investments Based on Market Conditions
- Rebalance your portfolio – Shift allocations if one stock sector becomes too dominant.
- Stay informed – Economic changes, corporate announcements, or global events can impact stocks.
- Review long-term goals – Ensure that your investment choices align with your financial objectives.
By placing well-thought-out trades and actively managing your investments, you can make informed decisions that support long-term wealth creation.
Step 8: Stay Informed and Keep Learning
Investing in the stock market is an ongoing learning process. The market is dynamic, influenced by economic trends, corporate performance, and global events. Staying informed and continuously improving your knowledge will help you make better investment decisions over time.
Importance of Continuous Education
- Market conditions change, and new investment opportunities arise regularly.
- Understanding financial concepts and strategies helps in risk management.
- Continuous learning builds confidence and prevents emotional decision-making.
Best Sources for Market News and Analysis
- Financial news websites – Economic Times, Moneycontrol, Bloomberg, and CNBC.
- Stock market apps – Most brokers provide real-time updates and analysis tools.
- Official company reports – Quarterly earnings reports and annual financial statements.
Recommended Books, Courses, and Financial Blogs
- Books: The Intelligent Investor by Benjamin Graham, One Up on Wall Street by Peter Lynch.
- Online courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and NSE Academy offer stock market courses.
- Blogs and podcasts: Trade Brains, Varsity by Zerodha, and Investing.com provide regular market insights.
Additional Tips for Beginners
- Start Small – Begin with a manageable amount and gradually increase investments as you gain experience.
- Avoid Speculation – Invest based on research, not hype or market rumors.
- Set Stop-Loss Limits – This prevents significant losses by automatically selling stocks if they drop beyond a set threshold.
- Diversify Your Portfolio – Spread investments across sectors to reduce risk.
- Seek Professional Advice – If unsure, consult a certified financial advisor to guide your investment strategy.
Conclusion
Investing in the Indian stock market can be rewarding, but it requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning. By following these steps—choosing a broker, opening an account, researching stocks, placing trades, and managing investments—you can build a solid foundation for your investment journey.
The key to success lies in informed decision-making and a long-term perspective. Stay committed, keep learning, and invest with confidence to achieve financial growth over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can a beginner start investing in the Indian stock market?
A beginner can start investing in the Indian stock market by following these steps:
- Choose a SEBI-registered broker (e.g., Zerodha, Upstox, Groww).
- Open a Demat and trading account with the broker.
- Complete the KYC process by submitting PAN, Aadhaar, and bank details.
- Deposit funds into the trading account.
- Research stocks and invest wisely, starting with blue-chip stocks or ETFs for lower risk.
- Monitor investments regularly and stay updated on market trends.
2. What are the key benefits of investing in the Indian stock market?
Investing in the stock market offers multiple benefits, including:
- Higher returns compared to traditional savings and fixed deposits.
- Ownership in top companies, gaining from their growth.
- Beating inflation, as stocks generally offer inflation-adjusted returns.
- Dividend income, generating passive earnings.
- Liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell stocks easily.
3. How much money is required to start investing in stocks in India?
Contrary to popular belief, investing in Indian stocks doesn’t require a large amount. Many brokers allow investments with as little as ₹100. Fractional investing, mutual funds, and ETFs enable small-capital investments while offering diversification.
4. What is the difference between a Demat account and a trading account?
- Demat Account: Acts as a digital locker, storing stocks electronically.
- Trading Account: Enables buying and selling of stocks on the NSE and BSE.
Both accounts are essential for stock market transactions and are often provided together by brokers.
5. What are the risks involved in stock market investing?
Stock market investing carries risks, including:
- Market volatility—Stock prices fluctuate based on economic conditions.
- Company-specific risks—Poor business performance can lead to losses.
- Liquidity risk—Some stocks may have low trading volumes, making selling difficult.
- Regulatory risks—Government policies and regulations can impact stock prices.
To minimize risks, investors should diversify portfolios, conduct thorough research, and invest based on long-term financial goals.
